密码学基础
密码学就是专门研究编制密码和破译密码的技术科学
openssl
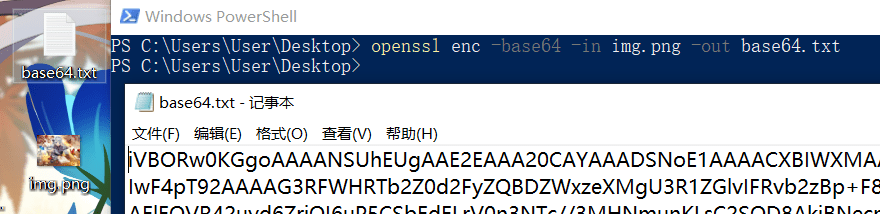
base64编码:
1 | openssl enc -base64 -in img.png -out base64.txt |
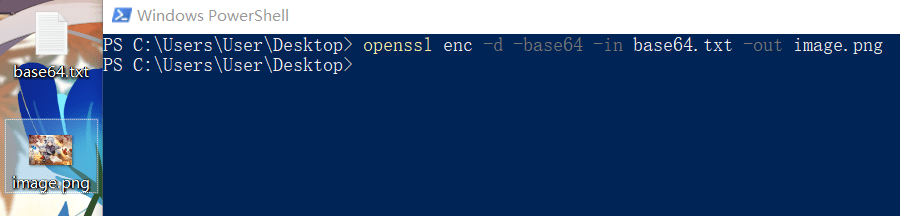
base64解码:
1 | openssl enc -d -base64 -in base64.txt -out image.png |
md5:
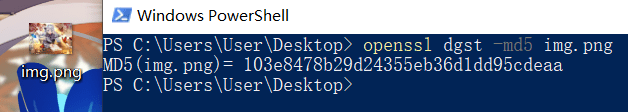
查看 md5 输出到控制台中:
1 | openssl dgst -md5 img.png |
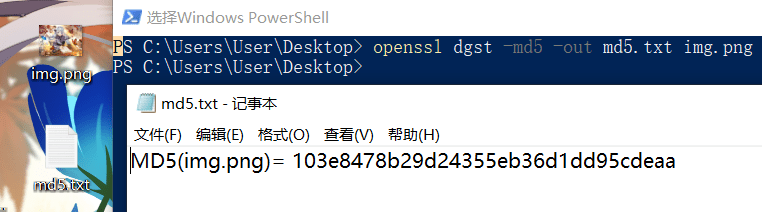
查看 md5 输出到文件中:
1 | openssl dgst -md5 -out md5.txt img.png |
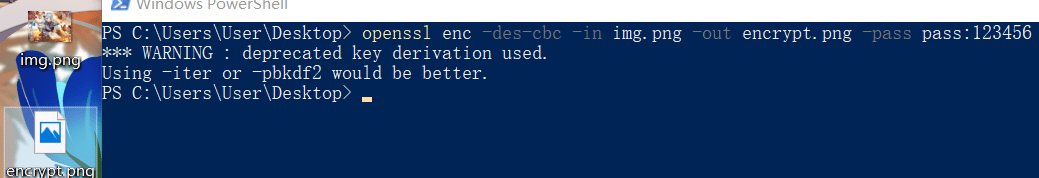
对称加密:
1 | openssl enc -des-cbc -in img.png -out encrypt.png -pass pass:123456 |
调用openssl的API
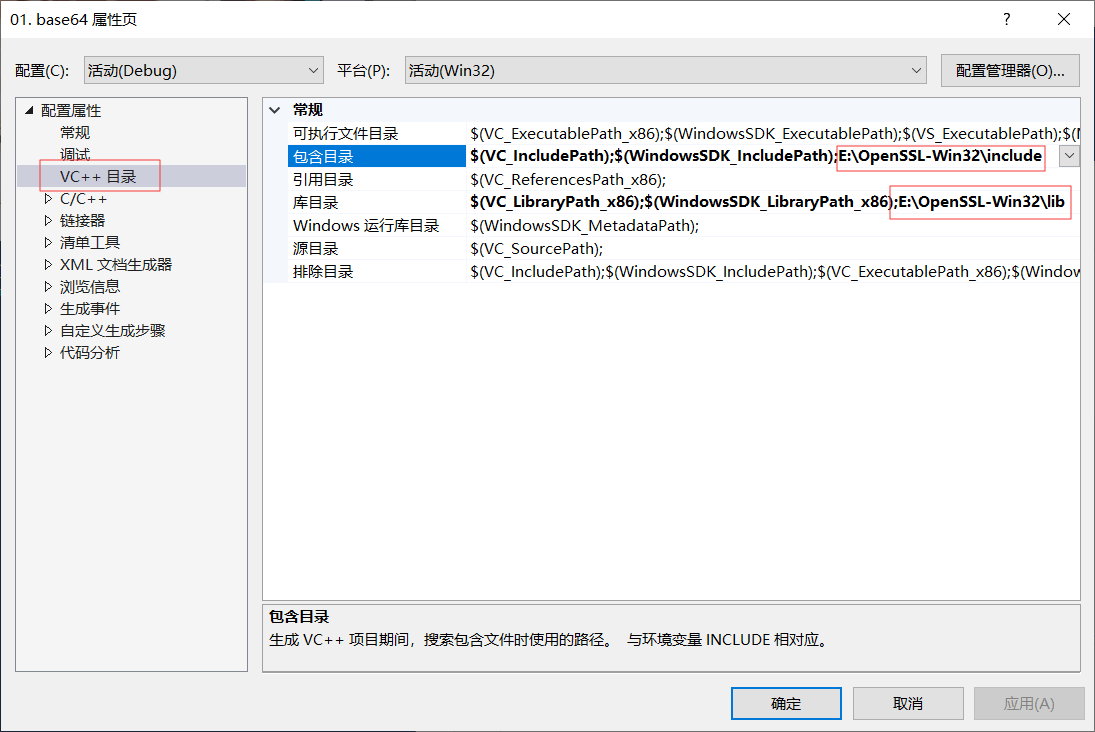
配置项目:
base64:
1 |
|
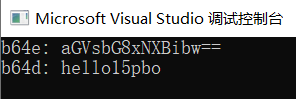
消息摘要:
1 |
|

aes:
1 |
|
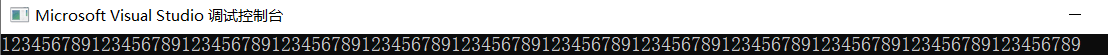
rsa:
1 |
|